Main points of management before the chicken lays eggs
A few weeks before chickens lay eggs, is considered the transitional period from the growth phase to the laying period. At this stage, a series of tasks such as putting the chickens into their cage, selection, immunization, changing the feed and increasing light will cause a great deal of responsibility.
During this period, the chicken’s physiology changes drastically. The chicken is sensitive and has weak adaptability and poor disease resistance. If the feeding and management are not up to par, this will adversely affect the performance of laying.
9 important points for improving the egg laying rate
1. Preparation
- Overhaul the chicken coop and equipment, and carefully check the chicken feeding system, drinking water system, power supply lighting, ventilation, drainage and cages, frame and other equipment. If there has been any abnormality this should be repaired promptly;
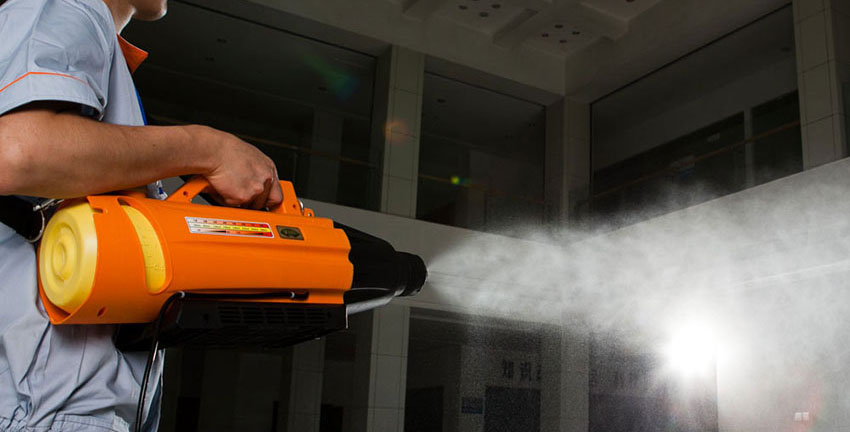
- Thoroughly clean and disinfect the chicken coop and equipment. Steps: first clean the feces, dust, and dirt on the floor, roof, and wall of the chicken coop. Then wash the chicken coop and equipment with a high-pressure washer. Finally, disinfect the chicken house and equipment.
- Prepare the necessary utensils, medicines, instruments, record forms and feed, and arrange the feeding personnel
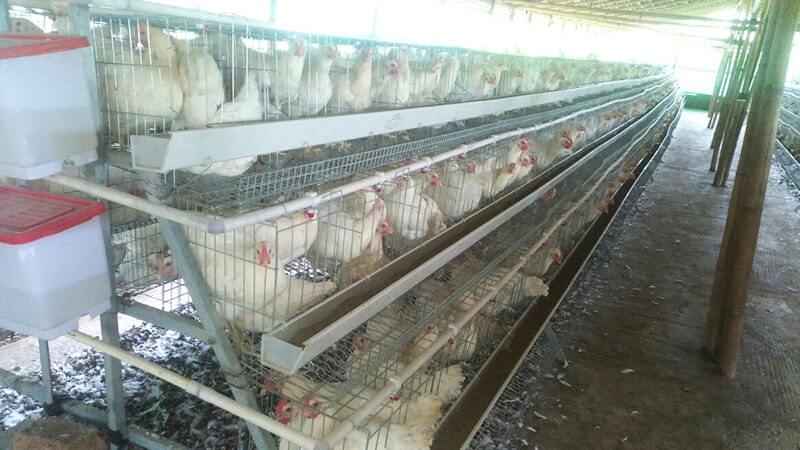
2. Transfer chicken to cage
1) Age of chicken transfer to cage
Chickens typically lay eggs at around 16 weeks, so they must be put into the cage before 15-16 weeks. This ensures that the hens have a period of time to become familiar with the environment before laying eggs. Then form a harmonious group sequence, and you will have enough time for immunization and other work. If chickens are put into cage too late, the egg laying time will be delayed and negatively affect the laying rate. The hens that have already been laying may be suspended due to high stress from being transferred. And some chickens may have yolk peritonitis and result in a significant increase in the number of dead chicken eggs.
- Selection
We require that the growth and development is good, even, and tidy. If uneven, it will seriously affect production performance. When putting chickens into cages, we should remove the undersized, thin, and stray chickens that have no breeding value, and choose high-quality chickens with lively spirit, strong constitution, and suitable weight.
- Classification
Even if the chicken in the brooding period is good, due to factors such as genetics and rearing management, there will still be some smaller and larger chickens in the flock. If we eliminate them, the cost will be increased and the cages in the layer house cannot be fully used. You will need to leave the smaller and larger chickens. Then put them into different cages separately. Take special measures to strengthen management to promote their uniformity. For example, put the smaller chickens in the middle cage with high temperature and exposure to the sun. Increase the nutrition properly to promote their growth and development. For large chickens, the number in the cage should be properly limited. According to the capacity of the cage, each single cage can be fed into a sufficient quantity at a time to avoid chickens that enter the cage first by bullying the chickens that enter the cage late.
3. Immunization
Immunization should be carried out before laying eggs. The immunization is essential to prevent the spread of diseases during egg production.
The immunization procedure is reasonable and conforms to the actual situation in the field. The vaccine source should be reliable, well preserved, and have quality assurance. The vaccination route should be appropriate and the operation done correctly with accurate dosage. After vaccination, you will need to check the effect of the vaccination. And if necessary, conduct antibody testing to ensure the effect of the vaccination, so that the chickens have sufficient antibody levels to prevent disease.
One method to improve the immune system is through respiratory administration. By dissolving the drug in water to use a fogger sprayer, when the chicken breathes the medicine will be in their body.
4. Expelling parasites
It should be done before laying eggs. For 110-130-day-old chickens, put 20-40 mg of levamisole or 200-300 mg of carbofuran per kilogram of body weight into the feed once a day for a total of 2 days to expel roundworms. Then put between 100-200 mg of bithionol per kilogram of body weight into the feed once a day for a total of 2 days to drive out tapeworms. When the oocysts of coccidioides are seriously polluted, the anti-coccidioides should be used continuously for 5 – 6 days after being put in the cage.
5. Light
Light has a great influence on the reproductive performance of chickens. Increasing light can stimulate the secretion of sex hormones to promote egg production. Shortening the light exposure will inhibit the secretion of sex hormones, thus inhibiting ovulation and egg production. By controlling the light exposed to the chicken this will stimulate and maintain the egg-laying balance. In addition, the light can adjust the sexual maturity of the reserve chickens and encourage the chicken to lay neatly. Light control is very critical when chickens are ready to lay. Appropriate light stimulation can ensure chickens lay properly beforehand and reduce feeding costs.
For chickens that meet the requirements or are slightly larger than the standard body weight, the light hours can be increased to 13 hours at around 16 – 17 weeks of age, and then increased by 20 minutes a week until the light hours reach 16 hours. The chickens with lower body weight should start light stimulation at around 18 – 20 weeks of age.
Light hours should increase gradually. If the exposure to light is too long, it’s easy to cause prolapse. Light intensity should be appropriate, not too strong or too weak. If too strong this will cause chickens to peck, and if too weak it is not effective.
Professional LED lights not only have a positive effect on the chicken laying rate, but also has good qualities to resist water, fire, and ammonia.
6. Breeding
Feeding before laying not only affects the laying rate and the duration of the peak laying period, but also affects the death rate.
1)Change feed in due course. In order to make hens more productive, reduce the rate of egg breakage, and reduce the occurrence of fatigue in laying hens, the calcium content in the diet should be increased from 0.9% to 2.5% from the age of 17 weeks. When the laying rate reaches 20% – 30%, the calcium content should increase to 3.5%.
2)Ensure feed intake. Before laying, you should let the chicken pick food freely, eat fully, ensure balanced nutrition, and promote the rate of laying.
3)Ensure drinking water. At the beginning of laying, the chicken has a strong metabolism and requires a significant amount of water. It is necessary to ensure adequate water. Insufficient water will affect the laying rate, and there will be more cases of prolapse of the anus.
7. Reduce stress
1) Arrange working time to reduce stress.
Putting chickens in cages and immunization is best done in the evening. Catch, transport, and put the chicken into the cage should be light. Before putting chickens into cages, you need to add feed in the feeder trough, water into the tank, and maintain the appropriate light intensity so that when chickens enter the cage they can drink water, eat feed, and get familiar with the environment as soon as possible. There should be a transitional period when changing the feed.
- Use anti-stress additives.
There are many stress factors before laying. Anti-stress agents can be added to the feed or drinking water to relieve stress. Vitamin C, instant multidimensional, fumaric acid, and sedative chlorpromazine are commonly used.
8. Sanitation
After entering the cage, the chicken is not familiar with the environment and this will cause great stress. As the rate of laying increases, the metabolism of the chicken is vigorous and the resistance is poor. It is extremely vulnerable to pathogens so it is necessary to strengthen resistance and immunity.
- Put an end to allowing the foreign staff into the feeding area and chicken house. The feeding staff need to be disinfected before entering;
- Pay attention to the chicken house environment, drinking water, and feed hygiene;
- Regularly disinfect the inside and outside of the house to reduce disease;
- Pay attention to the use of some antibacterial drugs and Chinese herbal medicines to prevent the occurrence of E. coli and mycoplasmosis.
9. Strengthen observation
Pay attention to the chicken feeding, respiration, feces and laying rate increases carefully, and find solutions to the problems promptly.
Before and after laying eggs, the physiology changes drastically, and the chickens are sensitive and uneasy. They are prone to getting hanging necks and winging. It is necessary to patrol more to detect and handle as soon as possible to reduce chances of death.
Pay attention, promptly find anal pecking chickens, bullied chickens, and sick and disabled chickens, and pick them out for treatment.
5 measures to improve the laying rate in summer
1. Control the temperature of the chicken house
- Reduce the heat radiation and reflection of the chicken house.
By planting trees around the chicken house or putting up shade, planting grass around the chicken house, painting the chicken house roof white or setting a ceiling, all these methods can reduce the radiation and reflect heat effectively to make the house cool.
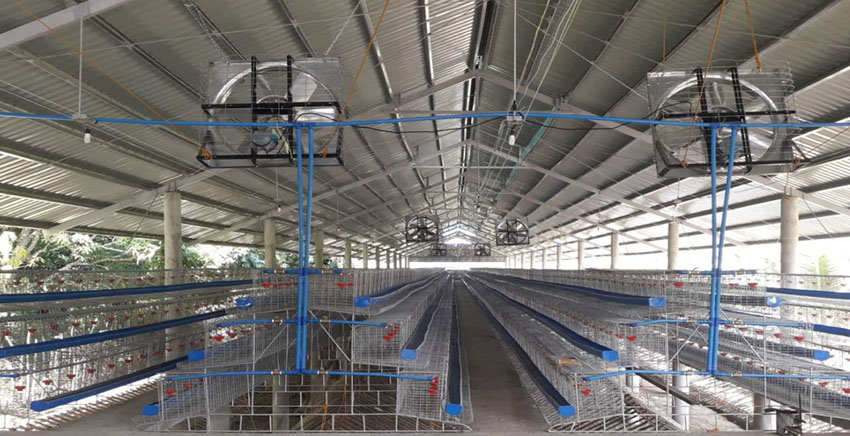
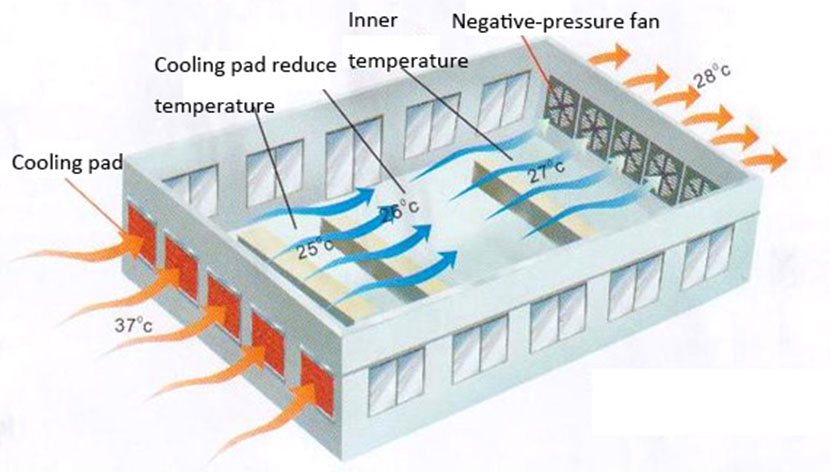
If you build enclosed chicken houses, you can use exhaust fans and cooling pads to make the house cool.
- Ventilation
By installing fans and water curtains, spraying water in the chicken house from time to time, enhancing ventilation etc. All methods can reduce the temperature of the house effectively.
- Reduce feeding density
Properly reduce the feeding density and reduce the chicken’s own heat production, so as to reduce the house temperature and reduce the impact of stress.
2. Strengthen feeding management
During the hot season, the temperature is higher around noon, therefore the chickens eat less, or even refuse to eat. You can adopt special feeding methods and change feeding times. For example, feed before 8 am and after 6 pm. Feed once more at night. Feeding less or no feeding at all from 8 am to 6 pm, but giving enough water (cold water is better). Where conditions permit, the powdered material can be changed to pellets, and the feed can be slightly moist. Increase the feed intake of the chicken, and reduce the effects of heat stress.
3. Adjust the feed
During the high-temperature season, the chickens eat relatively less. At this time, you can adjust the feed composition appropriately to ensure that the chickens get sufficient nutrition.
Adding 1% to 3% fat in the feed can not only increase the energy level of the feed, but also improve the palatability of the feed and increase the overall feed intake of the chicken.
Appropriately reduce the crude protein content in the feed and maintain the content of essential amino acids. You can add 0.1% to 1.5% methionine and 0.65% lysine.
4. Use anti-stress drugs and additives
- Add vitamins
Add enough vitamins to the feed, especially vitamin C and vitamin E.
Vitamin C can greatly improve the anti-stress ability of the chicken. Vitamin E helps the chicken to achieve the best immune functionality and improve the overall resistance to pathogens.
- Add granular calcium and electrolyte
The electrolytes not only make up for the lack of minerals and maintain the acid-base balance, but also improve the performance of the chicken undergoing heat stress. Adding the proper amount of granular calcium to the diet can supplement the low calcium levels in the blood. On the other hand, it can also increase the egg production rate and improve the quality of the eggshell.
5. Strengthen epidemic prevention and control the occurrence of diseases
Chickens get sick in summer easier, because mosquitoes breed and bacteria multiply quickly. It is necessary to strengthen the disinfection of chicken houses to prevent the spread of disease.
- Clean the house and cushion the sand soilfrequently to strengthen
- Adding fly maggot nets into the feed for 4 weeks can effectively reduce the breeding of mosquitoes and flies and significantly reduce the incidence of diseases spread by mosquitoes and flies.
- Addingastragalus polysaccharide, plant hemagglutinin, hypericin or ciprofloxacin lactate, lysozyme regularly in the feed can prevent the occurrence of bacterial and viral diseases.
- Proper vaccination is the key to prevent infectious diseases.
Hope this article was helpful and thanks for reading!














Leave A Comment